Solana Vs Ethereum: Which Good Contracts Blockchain Must You Pick?
October 18, 2022Лучшие Игровые Автоматы На Деньги Топ Слоты Для Игроков 202
November 19, 2022
Whether you’re a small, budding startup or a large, Fortune 100 conglomerate, you’re likely to come in contact with unearned revenue at some point. A common scenario that many technology startups have is when they have a platform that is sold to the customer for a monthly fee. An example of unearned revenue in this scenario would be if a customer were to purchase a full year of access to the company’s tech stack for $1200/year. In order to get this deal, the customer is required to pay the company in full on the spot.
What are the tax rules for deferred revenue?
The other side of the balancing entry is the revenue account (or accounts) flowing to the income statement. For example, a bakery company may need to take out a $100,000loan to continue business operations. Terms of the loan require equal annualprincipal repayments of $10,000 for the next ten years. Even though theoverall $100,000 note payable is considered long term, the $10,000required repayment during the company’s operating cycle isconsidered current (short term). This means $10,000 would beclassified as the current portion of a noncurrent note payable, andthe remaining $90,000 would remain a noncurrent note payable. When using financial information prepared by accountants,decision-makers rely on ethical accounting practices.
- For most companies, revenues come as a result of selling products or services.
- For example in air line industry, this liability arisen from tickets issued for future flights consists of almost 50% of total current liabilities.
- For example, unearned revenues may include rents received by a company or business for future periods or customer advances to book future sales.
- One of the most common answers to the question “What is unearned income?
Current Portion of a Note Payable

Revenue in https://www.bookstime.com/articles/accounting-for-medical-practices cash basis accounting is reported only after it’s been received. Expenses in cash basis accounting are recorded only when they’re paid as well. If you have noticed, what we are actually doing here is making sure that the earned part is included in income and the unearned part into liability. The adjusting entry will always depend upon the method used when the initial entry was made. The dividends declared by a company’s board of directors that have yet to be paid out to shareholders get recorded as current liabilities.

When advance cash is received from customer:
For example, unearned revenues may include rents received by a company or business for future periods or customer advances to book future sales. Other names used for this liability include unearned income, prepaid revenue, deferred revenue and customers’ deposits. While unearned revenue appears as cash in your account, in accounting terms, it’s considered a liability until your business delivers the goods or services as agreed. For this reason, it’s recorded as a current liability on your balance sheet and credited to your unearned revenue account, not your cash account. In summary, unearned revenue is a vital concept within accrual accounting, helping provide a more accurate representation of a company’s financial https://www.instagram.com/bookstime_inc position. By understanding and accurately recording unearned revenue, businesses can better manage cash flow and service obligations to their customers.

Supercharge your business’ finance journey
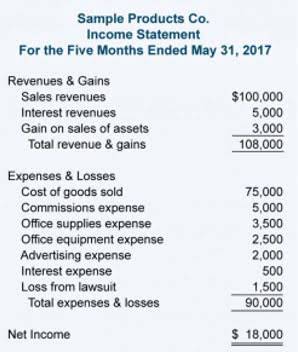
This journal entry illustrates that your business has received cash for its service that is earned on credit and considered a prepayment for future is unearned revenue a current liability goods or services rendered. Unearned revenue is usually disclosed as a current liability on a company’s balance sheet. This changes if advance payments are made for services or goods due to be provided 12 months or more after the payment date. In such cases, the unearned revenue will appear as a long-term liability on the balance sheet. Companies can’t record unearned revenues as sales because of the accruals concept of accounting.

